Basic Curiosity 2: What is photovoltaics?
- Ju Eun Yim

- Aug 4, 2019
- 2 min read
Updated: Aug 8, 2019
(Since now on, the post will be just a part of my study and its summary)
Photovoltaics
It is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect. Then, the photovoltaic effect is the creation of voltage and electric current in a material upon exposure to light. When the light is absorbed, it causes the excitation of an electron or other charge carrier to a higher-energy state. Then, electric potential is produced by the separation of charges. To maximize the efficiency of solar cells, it is important to choose a semiconductor material with an appropriate band gap that matches the solar spectrum. Improving the method of charge collection is also useful.
Inorganic semiconductors using GaAs and GaInP2 are ultrahigh efficiency devices. High-quality, single crystal silicon materials are also used.
Organic PV cells have made significant advancements in efficiency and cost.
Perovskite cells are also rapidly progressing between 2012 and 2018.
One of the major causes for the decreased performance of cells is overheating. The efficiency of a solar cell declines by about 0.5 % for every 1 ℃ increase in temperature. Rather than using energy to cool the surface, shaping silica to only absorb the visible light and reflect infrared rays (which carry heat) have been suggested for the solution.
Types of Solar Cells
Mono-/Multi- Crystalline silicon: As 1st generation module, mono(single)-crystalline shows high efficiency (avg. 14%) but, multi(poly)-crystalline is simpler, cheaper and environmentally cheaper to make.

CdTe (Cadmium telluride) and CIGS (Copper Indium Gallium Diselenide)
: As second-generation device, although these shows similar theoretical performance restrictions as 1st crystalline silicon-based device, the market expanded quickly due to low cost in manufacturing by reducing material and energy consumption. Theses films greatly reduced the thickness of modules and energy input. Still, the toxicity is an issue with CIGS because it contains Cd and Ga.

Perovskite PV cells
: As third-generation device, it is based on an organic-inorganic hybrid solar cell made of methylammonium lead halide perovskite. It shows no restriction (theoretically) in efficiency and the thickness is less than 1 micrometer. The major concern is its instability of lead exposed to environment.

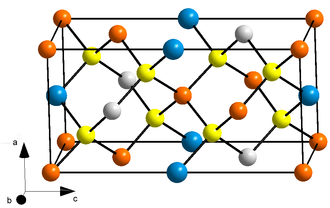
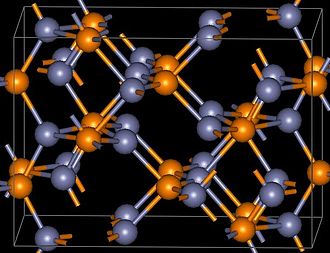
CZTS (Copper Zinc Tin Sulfide, Cu2ZnSnS4), Zinc Phosphide (Zn3P2) and single-walled carbon Nano-tubes (SWCNT)
: Currently produced only in lab, these thin films are made from earth abundant, nontoxic material and have the potential to produce more electricity annually than the current worldwide consumption. Their environmental impacts of commercial production and short lifetime are still needed to be studied.
The unit cell of CZTS (left) and Zinc Phosphide (right) from Wikipedia
Organic and polymer photovoltaic (OPV)
: As a relatively new area of research, it is cheaper to produce and more environmentally friendly. OPV are flexible and low in weights. The challenge is to increase its efficiency (currently 1-6.5%) and its lifetime.

There's so much room to improve!
Despite surpassing an efficiency limit previously considered insurmountable, solar cell viability is still fundamentally bounded by inconsistent weather conditions and availability of manufacturing materials. That is why we to develop energy storage devices, too. Moreover, both OPV electrodes and silicon solar cells require silver—a precious metal of which there simply isn’t enough to even make a dent in the global energy market.
[Reference Websites]



Comments